- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin as an Antiatherosclerotic Agent in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Review
Read this article at
Abstract
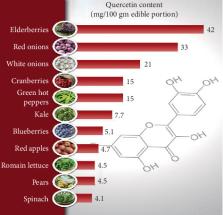
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is one of the diseases with the highest morbidity and mortality globally. It causes a huge burden on families and caregivers and high costs for medicine and surgical interventions. Given expensive surgeries and failures of most conventional treatments, medical community tries to find a more cost-effective cure. Thus, attentions have been primarily focused on food or herbs. Quercetin (Qu) extracted from food, a flavonoid component, develops potentials of alternative or complementary medicine in atherosclerosis. Due to the wide range of health benefits, researchers have considered to apply Qu as a natural compound in therapy. This review is aimed to identify the antiatherosclerosis functions of Qu in treating ASCVD such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties, effects on endothelium-dependent vasodilation, and blood lipid-lowering.
Related collections
Most cited references124

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A review of contemporary guidance and literature
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found