- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Novel extraction, rapid assessment and bioavailability improvement of quercetin: A review

Read this article at
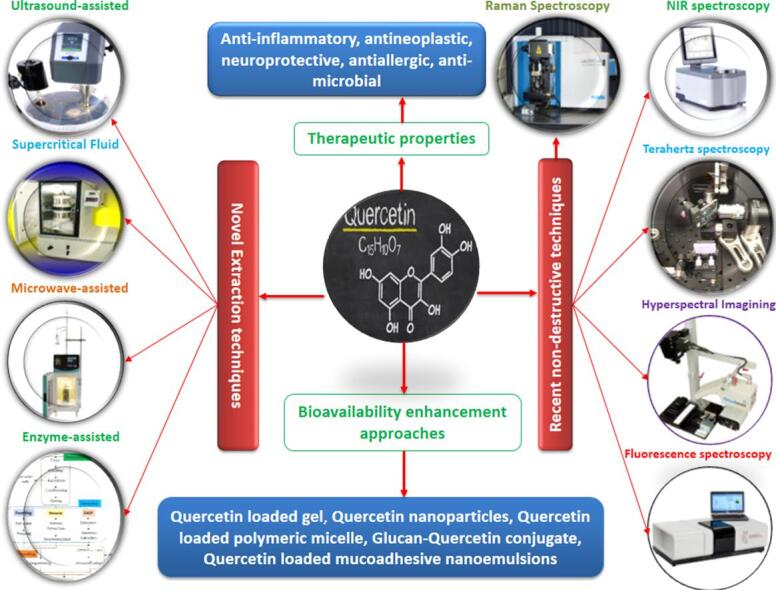
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Potential sources and therapeutic properties of quercetin.
-
•
In recent years, the different novel extractions techniques for the extraction of quercetin.
-
•
Non-destructive assessment techniques for the identification of quercetin in recent years.
-
•
Innovative drug delivery strategies to improve the bioavailability and providing novel therapeutic approaches.
Abstract
Quercetin (QUR) have got the attention of scientific society frequently due to their wide range of potential applications. QUR has been the focal point for research in various fields, especially in food development. But, the QUR is highly unstable and can be interrupted by using conventional assessment methods. Therefore, researchers are focusing on novel extraction and non-invasive tools for the non-destructive assessment of QUR. The current review elaborates the different novel extraction (ultrasound-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzyme-assisted extraction) and non-destructive assessment techniques (fluorescence spectroscopy, terahertz spectroscopy, near-infrared spectroscopy, hyperspectral imaging, Raman spectroscopy, and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy) for the extraction and identification of QUR in agricultural products. The novel extraction approaches facilitate shorter extraction time, involve less organic solvent, and are environmentally friendly. While the non-destructive techniques are non-interruptive, label-free, reliable, accurate, and environmental friendly. The non-invasive spectroscopic and imaging methods are suitable for the sensitive detection of bioactive compounds than conventional techniques. QUR has potential therapeutic properties such as anti-obesity, anti-diabetes, antiallergic, antineoplastic agent, neuroprotector, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities. Besides, due to the low bioavailability of QUR innovative drug delivery strategies (QUR loaded gel, QUR polymeric micelle, QUR nanoparticles, glucan-QUR conjugate, and QUR loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsions) have been proposed to improve its bioavailability and providing novel therapeutic approaches.
Related collections
Most cited references186
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging - Modern techniques and applications

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: a comprehensive review
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found