- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Community-Associated Bloodstream Infections in Zhejiang Province, China, 2017–2020
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
Community-associated bloodstream infection (CA-BSI) is increasing in many community settings. However, the clinical significance and epidemiology of CA-BSI present in hospital admissions in China are not well established. In this work, we identified the risk factors in outpatients presenting with CA-BSI, and investigate the role of procalcitonin (PCT) and hypersensitive C-reactive protein (CRP) in diagnosing different types of the pathogen in patients with acute CA-BSI.
Methods
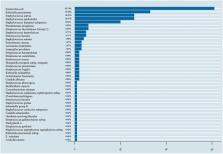
A retrospective study enrolling 219 outpatients with CA-BSI from The Zhejiang People’s Hospital from January 2017 to December 2020 was performed. Susceptibility of the isolates obtained from these patients was examined. Subjecting receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) were constructed to analyze the specificity and sensitivity of PCT, CRP, and WBC in determining infections caused by different bacterial genera. Risk factors for CA-BSI in the emergency setting were analyzed using essential information and simple identification of other pathogenic bacterial species through rapidly tested biomarkers.
Results
A total of 219 patients were included in the selection criteria, of which 103 were infected with Gram-positive bacteria (G+) and 116 with Gram-negative bacteria (G-). The PCT was significantly higher in the GN-BSI group than in the GP-BSI group, while no significant difference was observed between the two groups for CRP. Subjecting ROC curves were constructed to analyze WBC, CRP, and PCT, and the area under the curve (AUC) of the PCT in this model was 0.6661, with sensitivity = 0.798 and specificity = 0.489.
Conclusion
The PCT between the GP-BSI group and the GN-BSI group was significantly different. By combining the knowledge of clinicians and the clinical signs of patients, PCT should be utilized as a supplementary approach to initially determine pathogens and direct medication in the early stages of clinical practice.
Related collections
Most cited references32

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found