- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dietary intake of fish and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of postpartum depression: a nationwide longitudinal study – the Japan Environment and Children's Study (JECS)
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Pregnant women require increased levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) due to the demands of the growing fetus. Although some evidence indicates that maternal intake of fish and n-3 PUFAs is associated with reduced risk of postpartum depression, the results are inconsistent.
Methods
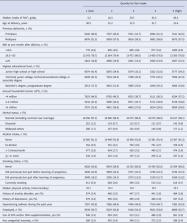
We investigated whether dietary consumption of fish and/or n-3 PUFAs during pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of maternal postpartum depression at 6 months after delivery and of serious mental illness at 1 year in a Japanese population. After exclusion and multiple imputation from a dataset comprising 103 062 pregnancies obtained in the Japan Environment and Children's Study, we evaluated 84 181 and 81 924 women at 6 months and 1 year after delivery, respectively.
Results
Multivariable logistic regression showed a reduced risk of postpartum depression at 6 months in the second to fifth quintiles v. the lowest quintile for fish and n-3 PUFA intake, with trend tests also revealing a significant linear association. At 1 year after delivery, fish intake was associated with a reduced risk of serious mental illness in the second to fifth quintiles v. the lowest quintile for fish and in the third to fifth quintiles v. the lowest quintile for n-3 PUFA intake, with trend tests also revealing a significant linear association.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found