- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy of an exoskeleton-based physical therapy program for non-ambulatory patients during subacute stroke rehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Individuals requiring greater physical assistance to practice walking complete fewer steps in physical therapy during subacute stroke rehabilitation. Powered exoskeletons have been developed to allow repetitious overground gait training for individuals with lower limb weakness. The objective of this study was to determine the efficacy of exoskeleton-based physical therapy training during subacute rehabilitation for walking recovery in non-ambulatory patients with stroke.
Methods
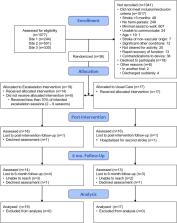
An assessor-blinded randomized controlled trial was conducted at 3 inpatient rehabilitation hospitals. Patients with subacute stroke (< 3 months) who were unable to walk without substantial assistance (Functional Ambulation Category rating of 0 or 1) were randomly assigned to receive exoskeleton-based or standard physical therapy during rehabilitation, until discharge or a maximum of 8 weeks. The experimental protocol replaced 75% of standard physical therapy sessions with individualized exoskeleton-based sessions to increase standing and stepping repetition, with the possibility of weaning off the device. The primary outcome was walking ability, measured using the Functional Ambulation Category. Secondary outcomes were gait speed, distance walked on the 6-Minute Walk Test, days to achieve unassisted gait, lower extremity motor function (Fugl-Meyer Assessment), Berg Balance Scale, Patient Health Questionnaire, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, and 36-Item Short Form Survey, measured post-intervention and after 6 months.
Results
Thirty-six patients with stroke (mean 39 days post-stroke) were randomized (Exoskeleton = 19, Usual Care = 17). On intention-to-treat analysis, no significant between-group differences were found in the primary or secondary outcomes at post-intervention or after 6 months. Five participants randomized to the Exoskeleton group did not receive the protocol as planned and thus exploratory as-treated and per-protocol analyses were undertaken. The as-treated analysis found that those adhering to exoskeleton-based physical therapy regained independent walking earlier (p = 0.03) and had greater gait speed (p = 0.04) and 6MWT (p = 0.03) at 6 months; however, these differences were not significant in the per-protocol analysis. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusions
This study found that exoskeleton-based physical therapy does not result in greater improvements in walking independence than standard care but can be safely administered at no detriment to patient outcomes.
Clinical Trial Registration The Exoskeleton for post-Stroke Recovery of Ambulation (ExStRA) trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02995265, first registered: December 16, 2016)
Related collections
Most cited references66
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found