- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
An intense form of homeostatic proliferation of naive CD8 + cells driven by IL-2
Read this article at
Abstract
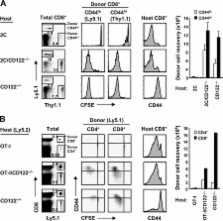
In conditions of T lymphopenia, interleukin (IL) 7 levels rise and, via T cell receptor for antigen–self–major histocompatibility complex (MHC) interaction, induce residual naive T cells to proliferate. This pattern of lymphopenia-induced “homeostatic” proliferation is typically quite slow and causes a gradual increase in total T cell numbers and differentiation into cells with features of memory cells. In contrast, we describe a novel form of homeostatic proliferation that occurs when naive T cells encounter raised levels of IL-2 and IL-15 in vivo. In this situation, CD8 + T cells undergo massive expansion and rapid differentiation into effector cells, thus closely resembling the T cell response to foreign antigens. However, the responses induced by IL-2/IL-15 are not seen in MHC-deficient hosts, implying that the responses are driven by self-ligands. Hence, homeostatic proliferation of naive T cells can be either slow or fast, with the quality of the response to self being dictated by the particular cytokine (IL-7 vs. IL-2/IL-15) concerned. The relevance of the data to the gradual transition of naive T cells into memory-phenotype (MP) cells with age is discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Defective TCR expression in transgenic mice constructed using cDNA-based alpha- and beta-chain genes under the control of heterologous regulatory elements.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
