- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Bioinformatic Analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
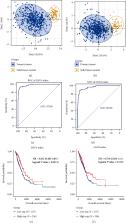
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), which accounts for 60% of non-small-cell lung cancers, is poorly diagnosed and has a low average 5-year survival rate (approximately 20%). It remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Studies on long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in LUAD-related competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks are limited. We aimed to identify novel prognostic biomarkers for LUAD using bioinformatic tools and data analysis. We systemically integrated differentially expressed genes and clinically significant modules using weighted correlation network analysis. We performed a functional analysis of the collected candidate genes and explored three LUAD-related genes ( VWF, PECAM1, and COL1A1) associated with the overall survival rates of patients with LUAD. Based on Cox proportional hazards analysis of candidate mRNAs and lncRNAs together with differentially expressed microRNAs, we constructed ceRNA networks, obtained 12 lncRNAs in the ceRNA networks, and revealed seven novel lncRNAs AC021016.2, AC079630.1, AC116407.1, AC125807.2, AF131215.5, LINC01936, and RHOXF1-AS1. These lncRNAs were found to be associated with overall survival rates and are suitable for the prediction of prognosis by Kaplan-Meier survival and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses. In particular, three lncRNAs— AF131215.5, AC125807.2, and LINC01936—showed an independent prognostic value of overall survival for patients with LUAD. We evaluated the diagnostic capabilities of seven lncRNAs for patients with LUAD using principal component analysis and the Gene Set Variation Analysis index. lncRNAs and crucial genes could be effectively used for distinguishing LUAD tumors from normal tissues in the Gene Expression Omnibus profile. In particular, AC021016.2 showed a significant prognostic value in the validation dataset. Our findings reveal the significance of exploring lncRNAs in cancer-related ceRNAs using bioinformatic strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found