- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Integrated bioinformatics analysis elucidates granulosa cell whole-transcriptome landscape of PCOS in China
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common reproductive, neuroendocrine, and metabolic disorder in women of reproductive age that affects up to 5–10% of women of reproductive age. The aetiology of follicle development arrest and critical issues regarding the abnormal follicular development in PCOS remain unclear. The present study aims to systematically evaluate granulosa cell whole-transcriptome sequencing data to gain more insights into the transcriptomic landscape and molecular mechanism of PCOS in China.
Methods
In the present study, the microarray datasets GSE138518, GSE168404, GSE193123, GSE138572, GSE95728, and GSE145296 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Subsequently, differential expression analysis was performed on the PCOS and control groups, followed by functional interaction prediction analysis to investigate gene-regulatory circuits in PCOS. Finally, hub genes and their associated ncRNAs were validated by qPCR in human-luteinized granulosa (hGL) cells and were correlated with the clinical characteristics of the patients.
Results
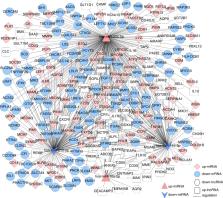
A total of 200 differentially expressed mRNAs, 3 differentially expressed miRNAs, 52 differentially expressed lncRNAs, and 66 differentially expressed circRNAs were found in PCOS samples compared with controls. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses indicated that the DEGs were mostly enriched in phospholipid metabolic processes, steroid biosynthesis and inflammation related pathways. In addition, the upregulated miRNA hsa-miR-205-5p was significantly enriched in the ceRNA network, and two hub genes, MVD and PNPLA3, were regulated by hsa-miR-205-5p, which means that hsa-miR-205-5p may play a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of PCOS. We also found that MVD and PNPLA3 were related to metabolic processes and ovarian steroidogenesis, which may be the cause of the follicle development arrest in PCOS patients.
Conclusions
In summary, we systematically constructed a ceRNA network depicting the interactions between the ncRNAs and the hub genes in PCOS and control subjects and correlated the hub genes with the clinical characteristics of the patients, which provides valuable insights into the granulosa cell whole-transcriptome landscape of PCOS in China.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Consensus on women's health aspects of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): the Amsterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored 3rd PCOS Consensus Workshop Group.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found