- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of Acute and Chronic Cannabis Use on Stress Response Regulation: Challenging the Belief That Cannabis Is an Effective Method for Coping
Read this article at
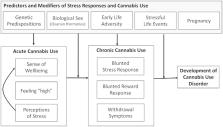
Abstract
Although research has only recently started to examine the impact of cannabis use on stress response, there is some evidence that indicates acute and chronic impacts of cannabis on these processes. In this paper, we review processes involved in regulating the stress response and we review the influence of acute and chronic exposure to cannabis on patterns and regulation of the stress response. We also highlight the role of stress as a risk factor for initiation and maintenance of cannabis use. In this context, we examine moderating variables, including sex and life adversity. In light of recent observations indicating increasing prevalence of cannabis use during pregnancy, we provide additional focus on cannabis use in this vulnerable population, including how acute and chronic stress may predispose some individuals to use cannabis during pregnancy. While this line of research is in its infancy, we review available articles that focus on the perinatal period and that examined the association between cannabis use and various life stressors, including partner violence, job loss, and lack of housing. We also review psychiatric co-morbidities (e.g., post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety). A better understanding of the way stress and cannabis use relate within the general population, as well as within certain subgroups that may be at a greater risk of using and/or at greater risk for adverse outcomes of use, may lead to the development of novel prevention and intervention approaches.
Related collections
Most cited references172
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: central role of the brain.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found