- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CT whole lung radiomic nomogram: a potential biomarker for lung function evaluation and identification of COPD
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
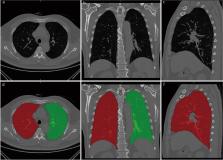
Computed tomography (CT) plays a great role in characterizing and quantifying changes in lung structure and function of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This study aimed to explore the performance of CT-based whole lung radiomic in discriminating COPD patients and non-COPD patients.
Methods
This retrospective study was performed on 2785 patients who underwent pulmonary function examination in 5 hospitals and were divided into non-COPD group and COPD group. The radiomic features of the whole lung volume were extracted. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression was applied for feature selection and radiomic signature construction. A radiomic nomogram was established by combining the radiomic score and clinical factors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the predictive performance of the radiomic nomogram in the training, internal validation, and independent external validation cohorts.
Results
Eighteen radiomic features were collected from the whole lung volume to construct a radiomic model. The area under the curve (AUC) of the radiomic model in the training, internal, and independent external validation cohorts were 0.888 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.869–0.906], 0.874 (95%CI 0.844–0.904) and 0.846 (95%CI 0.822–0.870), respectively. All were higher than the clinical model (AUC were 0.732, 0.714, and 0.777, respectively, P < 0.001). DCA demonstrated that the nomogram constructed by combining radiomic score, age, sex, height, and smoking status was superior to the clinical factor model.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Introduction to Radiomics
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found