- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Extract from Astragalus membranaceus inhibit breast cancer cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Astragalus membranaceus (AM) is a commonly used herb in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), which has been used as an essential tonic to treat various diseases for more than 2000 years. In this study, we aimed to investigate the biological effects of extract from AM on breast cancer cell and its mechanism.
Methods
To prepare the extract, dried AM were ground and extracted with water extraction-ethanol supernatant method. Then the main isoflavones in the extract was detect by HPLC analysis. Furthermore, the anti-proliferative activity of AM extract was examined by MTT assay and morphological observation. Cell apoptosis was evaluated with flow cytometric analysis. The expressions of total and phosphorylated PI3K, GS3Kβ, Akt and mTOR were determined by western blot analysis.
Results
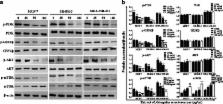
HPLC analysis demonstrated that AM extract contained with four kinds of isoflavones, campanulin, ononin, calycosin and formononetin. The MTT test and morphological observation indicated that cells proliferation of MCF-7, SK-BR-3 and MDA-MB-231were inhibited by AM extract in a dose dependent manner. Furthermore, flow cytometric analysis displayed that after treated with 25 μg/ml and 50 μg/ml AM extract, apoptosis of breast cancer cells was significantly increased as compared with DMSO and blank control group (all p < 0.05). Western blot analysis found that the level of p-PI3K, p-GS3Kβ, p-Akt, and p-mTOR were significantly decreased, but the level of total-mTOR was observably increased as compared with DMSO control group.
Conclusions
Taken together, the inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis effect of AM extract via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway confirmed the anti-tumor potential of AM. Therefore, our findings provide a new insight into anti-cancer effect of AM extract as a promising agent in breast cancer treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Incidence and Mortality and Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in the World.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found