- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Genomic Selection in the Era of Next Generation Sequencing for Complex Traits in Plant Breeding
Read this article at
Abstract
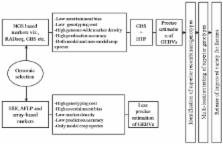
Genomic selection (GS) is a promising approach exploiting molecular genetic markers to design novel breeding programs and to develop new markers-based models for genetic evaluation. In plant breeding, it provides opportunities to increase genetic gain of complex traits per unit time and cost. The cost-benefit balance was an important consideration for GS to work in crop plants. Availability of genome-wide high-throughput, cost-effective and flexible markers, having low ascertainment bias, suitable for large population size as well for both model and non-model crop species with or without the reference genome sequence was the most important factor for its successful and effective implementation in crop species. These factors were the major limitations to earlier marker systems viz., SSR and array-based, and was unimaginable before the availability of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies which have provided novel SNP genotyping platforms especially the genotyping by sequencing. These marker technologies have changed the entire scenario of marker applications and made the use of GS a routine work for crop improvement in both model and non-model crop species. The NGS-based genotyping have increased genomic-estimated breeding value prediction accuracies over other established marker platform in cereals and other crop species, and made the dream of GS true in crop breeding. But to harness the true benefits from GS, these marker technologies will be combined with high-throughput phenotyping for achieving the valuable genetic gain from complex traits. Moreover, the continuous decline in sequencing cost will make the WGS feasible and cost effective for GS in near future. Till that time matures the targeted sequencing seems to be more cost-effective option for large scale marker discovery and GS, particularly in case of large and un-decoded genomes.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A vision for the future of genomics research.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found