- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Incidence of reactive hyperplastic lesions in the oral cavity: a 10 year retrospective study in Santa Catarina, Brazil ☆ Translated title: Incidência de lesões hiperplásicas reativas na cavidade bucal: estudo retrospectivo de 10 anos em Santa Catarina, Brasil
Abstract
Introduction
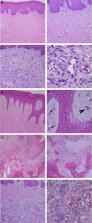
Reactive hyperplastic lesions develop in response to a chronic injury simulating an exuberant tissue repair response. They represent some of the most common oral lesions including inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia, oral pyogenic granuloma, giant cell fibroma, peripheral ossifying fibroma, and peripheral giant cell lesions.
Objective
The incidence of those lesions was investigated in an oral pathology service, and the clinical characteristics, associated etiological factors, concordance between the clinical and histopathological diagnostic was determined.
Methods
A total of 2400 patient records were screened from 2006 to 2016. Clinical features were recorded from biopsy reports and patients’ files.
Results
A total of 534 cases of reactive hyperplastic lesions were retrieved and retrospectively studied, representing 22.25% of all diagnoses. The most frequent lesion was inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia (72.09%), followed by oral pyogenic granuloma (11.79%), giant cell fibroma (7.30%), peripheral ossifying fibroma (5.24%), and peripheral giant cell lesions (3.55%). Females were predominantly affected (74.19%), the gingiva and alveolar ridge were the predominant anatomical site (32.89%), and chronic traumatism was presented as the main etiological factor. The age widely ranges from the 1st decade of life to the 7th. Clinically, the reactive hyperplastic lesions consisted of small lesions (0.5–2 cm) and shared a strong likeness in color to the oral mucosa. The concordance between the clinical and histopathological diagnostic was high (82.5%).
Conclusion
Reactive hyperplastic lesions had a high incidence among oral pathologies. The understanding of their clinical features helps to achieve a clearer clinical and etiological diagnosis, and the knowledge of factors related to their development. This may contribute to adequate treatment and positive prognosis.
Resumo
As lesões hiperplásicas reativas se desenvolvem em resposta a uma lesão crônica que estimula uma resposta acentuada de reparo tecidual. Elas representam uma das lesões orais mais comuns, inclusive a hiperplasia fibrosa inflamatória, granuloma piogênico oral, fibroma de células gigantes, fibroma periférico ossificante e lesão periférica de células gigantes.
A incidência dessas lesões foi investigada em um serviço de patologia bucal e as características clínicas, os fatores etiológicos associados e a concordância entre os diagnósticos clínico e histopatológico foram determinados.
Foram selecionados 2.400 registros de pacientes entre 2006 e 2016. As características clínicas foram registradas a partir de laudos de biópsia e dos prontuários dos pacientes.
Um total de 534 casos de lesões hiperplásicas reativas foram recuperados e retrospectivamente estudados, representando 22,25% de todos os diagnósticos. A lesão mais frequente foi hiperplasia fibrosa inflamatória (72,09%), seguida por granuloma piogênico oral (11,79%), fibroma de células gigantes, (7,30%), fibroma periférico ossificante (5,24%) e lesão periférica de células gigantes (3,55%). O sexo feminino foi predominante (74,19%), a gengiva e a crista alveolar foram o local anatômico predominante (32,89%) e o traumatismo crônico foi demonstrado como o principal fator etiológico. A idade variou desde a 1ª década de vida até a 7ª. Clinicamente, as LHR consistiram em pequenas lesões (0,5 a 2 cm) que apresentaram uma forte semelhança de cor com a mucosa oral. A concordância entre o diagnóstico clínico e histopatológico foi alta (82,5%).
As lesões hiperplásicas reativas apresentaram alta incidência entre as patologias bucais. A compreensão das características clínicas ajuda na realização de um diagnóstico clínico e etiológico mais claro, bem como determinar os fatores relacionados ao seu desenvolvimento. Dessa forma contribui para um tratamento adequado e um prognóstico positivo.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Oral pyogenic granuloma: Various concepts of etiopathogenesis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reactive lesions of the gingiva. A clinicopathological study of 741 cases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found