- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of alendronate or 8-prenylnaringenin applied as a single therapy or in combination with vibration on muscle structure and bone healing in ovariectomized rats
Read this article at
Abstract
Bisphosphonate alendronate (ALN), phytoestrogen 8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN) and the whole body vibration exert a favorable effect on osteoporotic bone. However, the impact of these treatments and the combination of pharmacological therapies with biomechanical stimulation on muscle and bone has not yet been explored in detail. The effect of ALN and 8-PN and their combination with the vibration (Vib) on skeletal muscle and bone healing was investigated in ovariectomized (Ovx) rats.
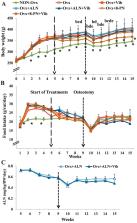
Three-month old rats were Ovx ( n = 78), or left intact (Non-Ovx; n = 12). Five weeks after Ovx, all rats were treated according to the group assignment (n = 12/13): 1) Non-Ovx; 2) Ovx; 3) Ovx + Vib; 4) Ovx + ALN; 5) Ovx + ALN + Vib; 6): Ovx + 8-PN; 7) Ovx + 8-PN + Vib. Treatments with ALN (0.58 mg/kg BW, in food), 8-PN (1.77 mg/kg BW, daily s.c. injections) and/or with vertical vibration (0.5 mm, 35 Hz, 1 g, 15 min, 2×/day, 5×/week) were conducted for ten weeks. Nine weeks after Ovx, all rats underwent bilateral tibia osteotomy with plate osteosynthesis and were sacrificed six weeks later.
Vibration increased fiber size and capillary density in muscle, enlarged callus area and width, and decreased callus density in tibia, and elevated alkaline phosphatase in serum. ALN and ALN + Vib enhanced capillarization and lactate dehydrogenase activity in muscle. In tibia, ALN slowed bone healing, ALN + Vib increased callus width and density, enhanced callus formation rate and expression of osteogenic genes. 8-PN and 8-PN + Vib decreased fiber size and increased capillary density in muscle; callus density and cortical width were reduced in tibia. Vibration worsened 8-PN effect on bone healing decreasing the callus width and area.
Our data suggest that Vib, ALN, 8-PN, or 8-PN + Vib do not appear to aid bone healing. ALN + Vib improved bone healing; however application is questionable since single treatments impaired bone healing. Muscle responds to the anti-osteoporosis treatments and should be included in the evaluation of the drugs.
Highlights
-
•
Vibration (Vib) was beneficial for muscle structure, it tended to interfere with early bone healing.
-
•
Alendronate (ALN) enhanced capillary density and metabolism in muscle, slowed bone healing.
-
•
8-Prenylnaringenin (8-PN) had favorable effects on muscle, for bone healing it was disadvantageous.
-
•
8PN + Vib further worsened 8-PN effect on bone, ALN + Vib improved bone healing.
-
•
Muscles respond to anti-osteoporosis treatments, their analysis should be included in the evaluation of drugs.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis in men.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found