- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Serological Response to the 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Virus for Disease Diagnosis and Estimating the Infection Rate in Thai Population
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Individuals infected with the 2009 pandemic virus A(H1N1) developed serological response which can be measured by hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) and microneutralization (microNT) assays.
Methodology/Principal Findings
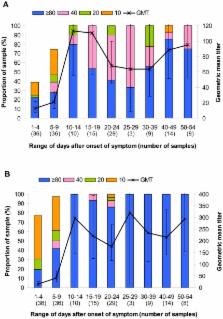
MicroNT and HI assays for specific antibody to the 2009 pandemic virus were conducted in serum samples collected at the end of the first epidemic wave from various groups of Thai people: laboratory confirmed cases, blood donors and health care workers (HCW) in Bangkok and neighboring province, general population in the North and the South, as well as archival sera collected at pre- and post-vaccination from vaccinees who received influenza vaccine of the 2006 season. This study demonstrated that goose erythrocytes yielded comparable HI antibody titer as compared to turkey erythrocytes. In contrast to the standard protocol, our investigation found out the necessity to eliminate nonspecific inhibitor present in the test sera by receptor destroying enzyme (RDE) prior to performing microNT assay. The investigation in pre-pandemic serum samples showed that HI antibody was more specific to the 2009 pandemic virus than NT antibody. Based on data from pre-pandemic sera together with those from the laboratory confirmed cases, HI antibody titers ≥40 for adults and ≥20 for children could be used as the cut-off level to differentiate between the individuals with or without past infection by the 2009 pandemic virus.
Related collections
Most cited references25
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cross-reactive antibody responses to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found