- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Short versus Long Antibiotic Course for Pleural Infection Management (SLIM) randomised controlled open-label trial
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Based on expert opinion, the length of antibiotic treatment for pleural infection in adults is typically recommended to be a minimum of 4 weeks. This clinical trial aimed to assess whether shorter antibiotic courses lead to more treatment failures than standard longer courses.
Methods
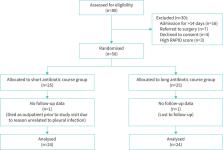
In an open-label randomised controlled trial, adult patients with pleural infection who were medically treated and stabilised within 14 days of admission were randomised to either a short antibiotic course (total course 14–21 days) or a long antibiotic course (total course 28–42 days). Patients were excluded if their baseline RAPID score was >4 (high-risk category). The primary outcome was the incidence of treatment failure by 6 weeks post-admission. Secondary outcomes were total length of antibiotic treatment, proportion of patients who resumed normal activity levels within 6 weeks post-admission, time from discharge to resuming normal activity levels and incidence of antibiotic-related adverse reactions.
Results
Between September 2020 and October 2021, 50 patients (mean± sd age 46±13.7 years; 35 (70%) males) were recruited to the trial and randomly assigned to the short course group (n=25) or the long course group (n=25), with outcome data available for 24 patients in each study group. Treatment failure occurred in four (16.7%) patients in the short course group and three (12.5%) patients in the long course group. In the intention-to-treat analysis the OR for treatment failure in the long course group was 0.714 (95% CI 0.142–3.600; p=0.683). The median (interquartile range) duration of antibiotic treatment in the short course group was 20.5 (18–22.5) days compared with 34.5 (32–38) days in the long course group (p<0.001). There were no statistically significant differences in the other outcomes.
Abstract
In medically treated adult patients with pleural infection, a long course of antimicrobial therapy does not lead to fewer treatment failures compared with a shorter course https://bit.ly/3JJHvxn
Related collections
Most cited references24

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
BTS guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in adults: update 2009.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found