- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Small airways dysfunction: The importance of utilising Z-scores to define MMEF abnormalities in clinical practice
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The small airways comprise the largest cross-sectional area of the lungs, however, assessing and reporting abnormalities for this region of the bronchial tree has been practically and scientifically uncertain.
Methods
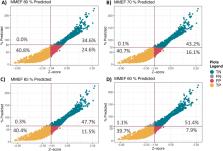
Using routinely collected spirometry data for patients with either asthma or COPD, the accuracy of % predicted values for defining small airways dysfunction was assessed. A z-score of ≤ −1.645 of the maximal-mid expiratory flow (MMEF) was used as the gold standard for defining abnormality in the small airways.
Results
Records of 3396 patients were included in the analysis. The false positive (FP) rates were 24.6 %, 16.1 %, 11.5 %, or 7.9 % when the % predicted value of 80 %, 70 %, 65 %, or 60 % were used, respectively. Sex, age, and BMI were associated with FP rates. Males were more likely to be categorised as FP with odds ratio (OR) between 1.10 and 1.49 across % predicted groups. Age was associated with FP rates with an OR between 1.01 and 1.08. The BMI was also associated with FP rates with an OR of 1.03 across all % predicted groups. Assessing the association of age groups with FP rate showed that those above 60 years old were more likely to be categorised as FP with an OR between 1.23 and 73.2 compared to those less than 30 years old.
Related collections
Most cited references23
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-yr age range: the global lung function 2012 equations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Exploring the relevance and extent of small airways dysfunction in asthma (ATLANTIS): baseline data from a prospective cohort study
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found