- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
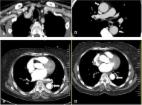
Limitations and Pitfalls of FDG-PET/CT in Infection and Inflammation
Jordy P. Pijl ,
Pieter H. Nienhuis ,
Thomas C. Kwee ,
Andor W.J.M. Glaudemans ,
Riemer H.J.A. Slart ,
Lars C. Gormsen
July 2021
July 2021
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references88
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: version 2.0
Ronald Boellaard, Roberto Delgado-Bolton, Wim Oyen … (2014)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Total-Body PET: Maximizing Sensitivity to Create New Opportunities for Clinical Research and Patient Care
Simon R Cherry, Terry Jones, Joel S Karp … (2018)