- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Imaging Hyperreflective Foci as an Inflammatory Biomarker after Anti-VEGF Treatment in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Patients with Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the hyperreflective foci (HRF) as an inflammatory biomarker using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) patients after antivascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) treatment and its association with the retinal microcapillary density.
Methods
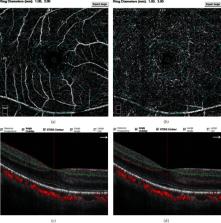
Twenty-five eyes from 25 patients with neovascular AMD were included in the study. All eyes were imaged with OCTA at baseline (M0) and after 3 consecutive injections (M3; injection performed each month) of anti-VEGF. The number of HRF in the superficial capillary plexus (SCP), deep capillary plexus (DCP), and outer retina was counted. The vascular density of the fovea, parafovea, and the whole macula, as well as the area of the foveal avascular zone (FAZ), was measured.
Results
The mean interval between baseline and follow-up with OCTA was 93.08 ± 5.00 (range, 85-101) days. Compared with the baseline, the number of HRF significantly decreased in DCP (7.52 ± 3.06 vs. 3.76 ± 1.48, P < 0.01) and outer retina (12.04 ± 4.91 vs. 5.88 ± 3.32, P < 0.01) after treatment. There was no significant difference for HRF number in the SCP, the vascular density (containing foveal, parafoveal, and whole macular), and FAZ area before and after treatments.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Microglia in neurodegenerative disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found