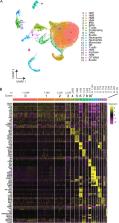
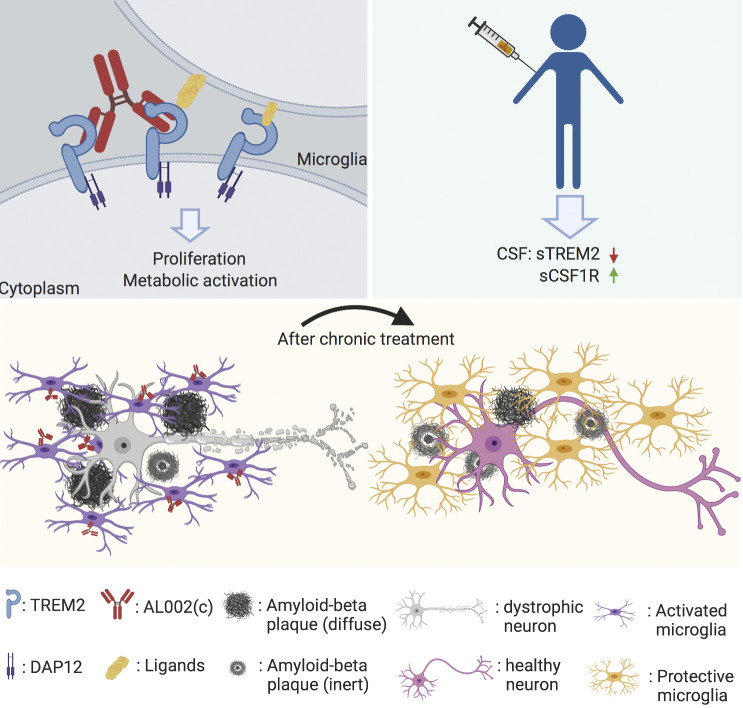
Shoutang Wang:
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1049-9127
Role: ConceptualizationRole: Data curationRole: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole:
MethodologyRole: ResourcesRole: SoftwareRole: ValidationRole: VisualizationRole: Writing
- original draftRole: Writing - review & editing
Meer Mustafa:
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2638-9523
Role: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole: Project administrationRole: SoftwareRole:
VisualizationRole: Writing - review & editing
Carla M. Yuede: Role: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole: Resources
Santiago Viveros Salazar: Role: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole: MethodologyRole: Visualization
Philip Kong: Role: InvestigationRole: Methodology
Hua Long: Role: Methodology
Michael Ward: Role: ConceptualizationRole: Data curationRole: InvestigationRole: MethodologyRole:
Project administrationRole: SupervisionRole: Writing - review & editing
Omer Siddiqui: Role: ConceptualizationRole: SupervisionRole: Writing - review & editing
Robert Paul: Role: InvestigationRole: MethodologyRole: Writing - original draftRole: Writing -
review & editing
Susan Gilfillan:
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1672-0996
Role: ResourcesRole: Writing - review & editing
Adiljan Ibrahim: Role: Resources
Hervé Rhinn: Role: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole: Methodology
Ilaria Tassi: Role: ConceptualizationRole: Project administrationRole: ResourcesRole: SupervisionRole:
ValidationRole: VisualizationRole: Writing - original draftRole: Writing - review
& editing
Arnon Rosenthal: Role: ConceptualizationRole: Funding acquisitionRole: ResourcesRole: SupervisionRole:
Writing - review & editing
Tina Schwabe: Role: ConceptualizationRole: Data curationRole: Formal analysisRole: InvestigationRole:
MethodologyRole: Project administrationRole: ResourcesRole: SupervisionRole: ValidationRole:
VisualizationRole: Writing - review & editing
Marco Colonna:
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5222-4987
Role: ConceptualizationRole: Funding acquisitionRole: SupervisionRole: Writing - original
draftRole: Writing - review & editing
Journal ID (nlm-ta): J Exp Med
Journal ID (iso-abbrev): J. Exp. Med
Journal ID (publisher-id): jem
Title:
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
Publisher:
Rockefeller University Press
ISSN
(Print):
0022-1007
ISSN
(Electronic):
1540-9538
Publication date Collection: 07
September
2020
Publication date
(Electronic):
24
June
2020
Volume: 217
Issue: 9
Electronic Location Identifier: e20200785
Affiliations
[1
]Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine,
St Louis, MO
[2
]Alector LLC, South San Francisco, CA
[3
]Department of Psychiatry and Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine,
St Louis, MO
Author notes
[*]
S. Wang and M. Mustafa contributed equally to this paper.
Disclosures: M. Mustafa, S.V. Salazar, P. Kong, H. Long, M. Ward, O. Siddiqui, R.
Paul, A. Ibrahim, H. Rhinn, I. Tassi, A. Rosenthal, and T. Schwabe reported "other"
from Alector, Inc. during the conduct of the study. The authors are employees of Alector
LLC and may have an equity interest in Alector, Inc. Alector and AbbVie are parties
to an agreement relating to the development and commercialization of AL002. M. Colonna
reported "other" from Alector and grants from Alector, Amgen, and Ono during the conduct
of the study. In addition, Alector LLC has pending patent applications and M. Colonna
has a patent to TREM2 pending. No other disclosures were reported.
Author information
Article
Publisher ID:
jem.20200785
DOI: 10.1084/jem.20200785
PMC ID: 7478730
PubMed ID: 32579671
SO-VID: 12be2e82-de31-4b08-b2ab-d88a34af3c4a
Copyright © © 2020 Wang et al.
License:
This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share
Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date
(see
http://www.rupress.org/terms/). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share
Alike 4.0 International license, as described at
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).
Funded by: National Institutes of Health, DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.13039/100000002;
Award ID: RF1AG05148501
Award ID: R21 AG059176
Award ID: RF1 AG059082
Funded by: Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.13039/100007625;