- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Monocyte and Macrophage miRNA: Potent Biomarker and Target for Host-Directed Therapy for Tuberculosis
Read this article at
Abstract
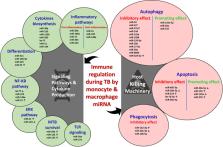
The end TB strategy reinforces the essentiality of readily accessible biomarkers for early tuberculosis diagnosis. Exploration of microRNA (miRNA) and pathway analysis opens an avenue for the discovery of possible therapeutic targets. miRNA is a small, non-coding oligonucleotide characterized by the mechanism of gene regulation, transcription, and immunomodulation. Studies on miRNA define their importance as an immune marker for active disease progression and as an immunomodulator for innate mechanisms, such as apoptosis and autophagy. Monocyte research is highly advancing toward TB pathogenesis and biomarker efficiency because of its innate and adaptive response connectivity. The combination of monocytes/macrophages and their relative miRNA expression furnish newer insight on the unresolved mechanism for Mycobacterium survival, exploitation of host defense, latent infection, and disease resistance. This review deals with miRNA from monocytes, their relative expression in different disease stages of TB, multiple gene regulating mechanisms in shaping immunity against tuberculosis, and their functionality as biomarker and host-mediated therapeutics. Future collaborative efforts involving multidisciplinary approach in various ethnic population with multiple factors (age, gender, mycobacterial strain, disease stage, other chronic lung infections, and inflammatory disease criteria) on these short miRNAs from body fluids and cells could predict the valuable miRNA biosignature network as a potent tool for biomarkers and host-directed therapy.
Related collections
Most cited references123

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found