- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Regenerative and translational medicine in COPD: hype and hope
Read this article at
Abstract
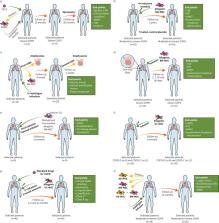
COPD is a common, preventable and usually progressive disease associated with an enhanced chronic inflammatory response in the airways and lung, generally caused by exposure to noxious particles and gases. It is a treatable disease characterised by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation due to abnormalities in the airways and/or alveoli. COPD is currently the third leading cause of death worldwide, representing a serious public health problem and a high social and economic burden. Despite significant advances, effective clinical treatments have not yet been achieved. In this scenario, cell-based therapies have emerged as potentially promising therapeutic approaches. However, there are only a few published studies of cell-based therapies in human patients with COPD and a small number of ongoing clinical trials registered on clinicaltrials.gov. Despite the advances and interesting results, numerous doubts and questions remain about efficacy, mechanisms of action, culture conditions, doses, timing, route of administration and conditions related to homing and engraftment of the infused cells. This article presents the state of the art of cell-based therapy in COPD. Clinical trials that have already been completed and with published results are discussed in detail. We also discuss the questions that remain unanswered about cell-based regenerative and translational medicine for COPD.
Tweetable abstract
This review describes the current state of the art of cell-based, regenerative and translational medicine in COPD, presenting the clinical trials already completed and with published results. https://bit.ly/3P08Bmq
Related collections
Most cited references139
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
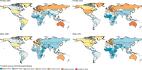
Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found