- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Methyltransferase-Like 3-Mediated m6A Methylation of Hsa_circ_0058493 Accelerates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Binding to YTH Domain-Containing Protein 1
Read this article at
Abstract
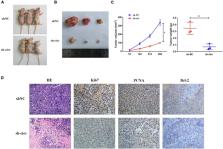
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are highly correlated with the progression and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In addition, mounting evidence has revealed that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation, a common RNA modification, is involved in the progression of malignancies. In this research, a novel circRNA, hsa_circ_0058493, was proven to be upregulated in HCC, which was correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Experimentally, hsa_circ_0058493 knockdown suppressed the growth and metastasis of HCC cells in vivo and in vitro. On the contrary, the overexpression of hsa_circ_0058493 in HCC cells had the opposite effect in vitro. Mechanistic experiments revealed that hsa_circ_0058493 contained m6A methylation sites and that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) mediated the degree of methylation modification of hsa_circ_0058493. Furthermore, YTH domain-containing protein 1 (YTHDC1) could bind to hsa_circ_0058493 and promote its intracellular localization from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. In addition, both si-METTL3 and si-YTHDC1 suppressed HCC cell growth and metastasis, whereas rescue experiments confirmed that overexpression of hsa_circ_0058493 inverted the inhibitory effects of si-METTL3 and si-YTHDC1 on HCC cells. Taken together, this study explored the oncogenic role of m6A-modified hsa_circ_0058493 and found to accelerate HCC progression via the METTL3-hsa_circ_0058493-YTHDC1 axis, indicating a potential therapeutic target for this deadly disease.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
m6A Modification in Coding and Non-coding RNAs: Roles and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found