- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sedative-Hypnotic and Receptor Binding Studies of Fermented Marine Organisms
Read this article at
Abstract
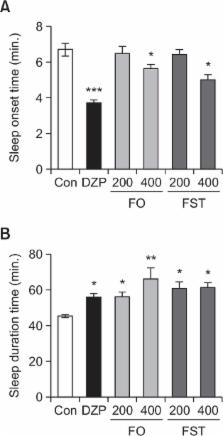
This study was performed to investigate the sedative-hypnotic activity of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-enriched fermented marine organisms (FMO), including sea tangle (FST) and oyster (FO) by Lactobacillus brevis BJ20 (L. brevis BJ20). FST and FO were tested for their binding activity of the GABA A-benzodiazepine and 5-HT 2C receptors, which are well-known molecular targets for sleep aids. We also measured the sleep latency and sleep duration during pentobarbital-induced sleep in mice after oral administration of FST and FO. In GABA A and 5-HT 2C receptor binding assays, FST displayed an effective concentration-dependent binding affinity to GABA A receptor, similar to the binding affinity to 5-HT 2C receptor. FO exhibited higher affinity to 5-HT 2C receptor, compared with the GABA A receptor. The oral administration of FST and FO produced a dose-dependent decrease in sleep latency and increase in sleep duration in pentobarbital-induced hypnosis. The data demonstrate that FST and FO possess sedative-hypnotic activity possibly by modulating GABA A and 5-HT 2C receptors. We propose that FST and FO might be effective agents for treatment of insomnia.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Antioxidant activity and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content in sea tangle fermented by Lactobacillus brevis BJ20 isolated from traditional fermented foods
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Serotonin2C receptor localization in GABA neurons of the rat medial prefrontal cortex: implications for understanding the neurobiology of addiction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found