- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dynamic association of PfEMP1 and KAHRP in knobs mediates cytoadherence during Plasmodium invasion
Read this article at
Abstract
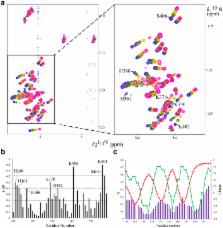
Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes display membrane knobs that are essential for their adherence to vascular endothelia and for prevention of clearance by the spleen. The knob associated histidine rich protein (KAHRP) is indispensable to knob formation and has been implicated in the recruitment and tethering of P. falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein–1 (PfEMP1) by binding to its cytoplasmic domain termed VARC. However, the precise mechanism of interaction between KAHRP and VARC is not very well understood. Here we report that both the proteins co-localize to membrane knobs of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes and have identified four positively charged linear sequence motifs of high intrinsic mobility on KAHRP that interact electrostatically with VARC in solution to form a fuzzy complex. The current study provides molecular insight into interaction between KAHRP and VARC in solution that takes place at membrane knobs.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE assignment using the new software CANDID and the torsion angle dynamics algorithm DYANA.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cloning the P. falciparum gene encoding PfEMP1, a malarial variant antigen and adherence receptor on the surface of parasitized human erythrocytes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The large diverse gene family var encodes proteins involved in cytoadherence and antigenic variation of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.