- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Gender, Culture, and Sex-Typed Cognitive Abilities
Read this article at
Abstract
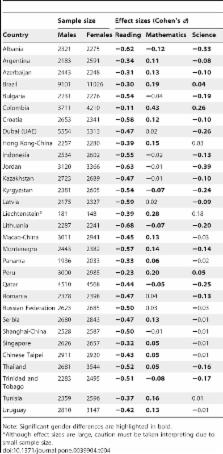
Although gender differences in cognitive abilities are frequently reported, the magnitude of these differences and whether they hold practical significance in the educational outcomes of boys and girls is highly debated. Furthermore, when gender gaps in reading, mathematics and science literacy are reported they are often attributed to innate, biological differences rather than social and cultural factors. Cross-cultural evidence may contribute to this debate, and this study reports national gender differences in reading, mathematics and science literacy from 65 nations participating in the 2009 round of the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). Consistently across all nations, girls outperform boys in reading literacy, d = −.44. Boys outperform girls in mathematics in the USA, d = .22 and across OECD nations, d = .13. For science literacy, while the USA showed the largest gender difference across all OECD nations, d = .14, gender differences across OECD nations were non-significant, and a small female advantage was found for non-OECD nations, d = −.09. Across all three domains, these differences were more pronounced at both tails of the distribution for low- and high-achievers. Considerable cross-cultural variability was also observed, and national gender differences were correlated with gender equity measures, economic prosperity, and Hofstede’s cultural dimension of power distance. Educational and societal implications of such gender gaps are addressed, as well as the mechanisms by which gender differences in cognitive abilities are culturally mediated.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A threat in the air. How stereotypes shape intellectual identity and performance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found