- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Susceptibility of Trypanosomatid Pathogens to PI3/mTOR Kinase Inhibitors Affords a New Opportunity for Drug Repurposing
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Target repurposing utilizes knowledge of “druggable” targets obtained in one organism and exploits this information to pursue new potential drug targets in other organisms. Here we describe such studies to evaluate whether inhibitors targeting the kinase domain of the mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) and human phosphoinositide-3-kinases (PI3Ks) show promise against the kinetoplastid parasites Trypanosoma brucei, T. cruzi, Leishmania major, and L. donovani. The genomes of trypanosomatids encode at least 12 proteins belonging to the PI3K protein superfamily, some of which are unique to parasites. Moreover, the shared PI3Ks differ greatly in sequence from those of the human host, thereby providing opportunities for selective inhibition.
Methodology/Principal Findings
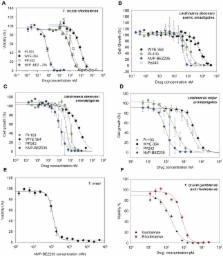
We focused on 8 inhibitors targeting mTOR and/or PI3Ks selected from various stages of pre-clinical and clinical development, and tested them against in vitro parasite cultures and in vivo models of infection. Several inhibitors showed micromolar or better efficacy against these organisms in culture. One compound, NVP-BEZ235, displayed sub-nanomolar potency, efficacy against cultured parasites, and an ability to clear parasitemia in an animal model of T. brucei rhodesiense infection.
Conclusions/Significance
These studies strongly suggest that mammalian PI3/TOR kinase inhibitors are a productive starting point for anti-trypanosomal drug discovery. Our data suggest that NVP-BEZ235, an advanced clinical candidate against solid tumors, merits further investigation as an agent for treating African sleeping sickness.
Author Summary
In our study we describe the potency of established phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) and mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) kinase inhibitors against three trypanosomatid parasites: Trypanosoma brucei, T. cruzi, and Leishmania sp., which are the causative agents for African sleeping sickness, Chagas disease, and leishmaniases, respectively. We noted that these parasites and humans express similar kinase enzymes. Since these similar human targets have been pursued by the drug industry for many years in the discovery of cellular growth and proliferation inhibitors, compounds developed as human anti-cancer agents should also have effect on inhibiting growth and proliferation of the parasites. With that in mind, we selected eight established PI3K and mTOR inhibitors for profiling against these pathogens. Among these inhibitors is an advanced clinical candidate against cancer, NVP-BEZ235, which we demonstrate to be a highly potent trypanocide in parasite cultures, and in a mouse model of T. brucei infection. Additionally, we describe observations of these inhibitors' effects on parasite growth and other cellular characteristics.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Visceral leishmaniasis: what are the needs for diagnosis, treatment and control?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found