- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Biosynthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles from Mentha spicata and screening its combating potential against Phytophthora infestans
Read this article at
Abstract
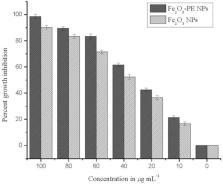
Plant pathogens cause serious diseases to agricultural crops which lead to food insecurity in the world. To combat plant pathogens, various strategies have been developed including the use of agrochemicals. The overuse of these chemicals is now leading to the pesticide-resistant capability of pathogens. To overcome this problem, modern nanobiotechnology offers the production of alternative nano drugs. In this study, we used Mentha spicata for the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using the green synthesis method. The synthesis of Fe 2O 3 NPs was confirmed through various characterizations. UV–Vis analysis detected a characteristic absorbance at the spectral range of 272 nm. The SEM micrographic analysis at various magnifications displayed circular or rod-shaped nanoparticles with a size ranging from 21 to 82 nm. The elemental EDX characterization showed intense peaks with a weight percent of 57, 34.93, and 8.07 for Fe, O, and, Cl respectively. TGA analysis showed that weight loss at 44–182, 500, and 660°C with no further modification indicates the thermal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles. FTIR spectrum of uncalined detects various bands at 3331, 1625, and 1,437 cm −1 for the hydroxyl group. After calcination two bands at 527 and 434 cm −1 were observed for Fe-O. The antimicrobial in vitro study showed maximum growth inhibition of Phytophthora infestans by the concentration of 100 μg ml −1 of Fe 2O 3-PE and Fe 2O 3 NPs. Therefore, this study resulted that bio-stable iron oxide nanoparticles can be used as alternative antimicrobial agents.
Related collections
Most cited references52
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles and Their Environmental Applications and Implications
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found