- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Enabling reversible redox reactions in electrochemical cells using protected LiAl intermetallics as lithium metal anodes
Read this article at
Abstract
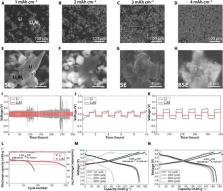
MoS 2 protected LiAl intermetallic compound Li metal anode exhibits a highly reversible Li migration for lithium metal batteries.
Abstract
Rechargeable electrochemical cells with metallic anodes are of increasing scientific and technological interest. The complex composition, poorly defined morphology, heterogeneous chemistry, and unpredictable mechanics of interphases formed spontaneously on the anodes are often examined but rarely controlled. Here, we couple computational studies with experimental analysis of well-defined LiAl electrodes in realistic electrochemical environments to design anodes and interphases of known composition. We compare phase behavior, Li binding energies, and activation energy barriers for adatom transport and study their effects on the electrochemical reversibility of battery cells. As an illustration of potential practical benefits of our findings, we create cells in which LiAl anodes protected by Langmuir-Blodgett MoS 2 interphases are paired with 4.1 mAh cm −2 LiNi 0.8Co 0.1Mn 0.1O 2 cathodes. These studies reveal that small- and larger-format (196 mAh, 294 Wh kg −1, and 513 Wh liter −1) cells based on protected LiAl anodes exhibit high reversibility and support stable Li migration during recharge of the cells.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pathways for practical high-energy long-cycling lithium metal batteries
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Selective deposition and stable encapsulation of lithium through heterogeneous seeded growth
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found