- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Screen time increases overweight and obesity risk among adolescents: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Adolescence is a critical period in human life, associated with reduced physical activity and increased sedentary behaviors. In this systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis, we evaluated the association between screen time and risk of overweight/obesity among adolescents.
Methods
A systematic search in electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and Scopus was performed up to September 2021. All published studies evaluating the association between screen time and risk of overweight/obesity among adolescents were retrieved. Finally, a total of 44 eligible studies were included in the meta-analysis.
Results
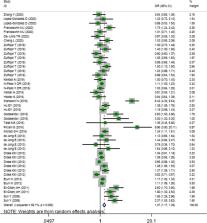
The results of the two-class meta-analysis showed that adolescents at the highest category of screen time were 1.27 times more likely to develop overweight/obesity (OR = 1.273; 95% CI = 1.166–1.390; P < 0.001; I-squared (variation in ES attributable to heterogeneity) = 82.1%). The results of subgrouping showed that continent and setting were the possible sources of heterogeneity. Moreover, no evidence of non-linear association between increased screen time and risk of overweight/obesity among adolescents was observed (P-nonlinearity = 0.311).
Conclusion
For the first time, the current systematic review and meta-analysis revealed a positive association between screen time and overweight/obesity among adolescents without any dose-response evidence.
Trial registration
The protocol of the current work has been registered in the PROSPERO system (Registration number: CRD42021233899).
Related collections
Most cited references84
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found