- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Changes in Menopausal Risk Factors in Early Postmenopausal Osteopenic Women After 13 Months of High-Intensity Exercise: The Randomized Controlled ACTLIFE-RCT
Abstract
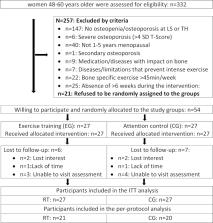
The menopausal transition is a critical period in women’s lives. Exercise might be the most promising non-pharmaceutic intervention to address the large variety of risk factors related to the pronounced estradiol decline during peri- and early-postmenopause. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of an 18-month multipurpose exercise program on risk factors and symptoms related to the menopausal transition. Fifty-four women 1–5 years postmenopause with osteopenia or osteoporosis were randomly assigned 1) to a high impact weight-bearing/high-intensity/velocity resistance training group (EG: n=27) exercising three times a week or 2) to an attendance control group (CG: n=27) that performed low-intensity exercise once a week. Both groups were supplemented with cholecalciferol and calcium. The primary study endpoint was bone mineral density (BMD) at lumbar spine (LS) and total hip, secondary outcomes were lean body mass (LBM), total and abdominal body percentage, metabolic syndrome Z-Score (MetS-Z), menopausal symptoms and muscle strength and power. Due to COVID-19, the study was stopped after 13 months. We observed significant effects for BMD-LS (EG: 0.002±.018 versus CG: −.009±0.018 mg/cm2, p=0.027) but not for BMD total hip (EG: −0.01±.016 versus CG: −.009±0.020 mg/cm2, p=0.129). LBM improved significantly in the EG and decreased in the CG (0.39±1.08 vs −0.37±1.34 kg, p=0.026). Total and abdominal body fat improved significantly in the EG and was maintained in the CG (−1.44±1.49 vs −0.02±1.55 kg, p=0.002 and -1.50±2.33 vs 0.08±2.07 kg, p=0.011). Significant effects in favor of the EG were also determined for menopausal symptoms (p=0.029), hip/leg extension strength (p<0.001) and power (p<0.001). However, changes of the MetS-Z did not differ significantly (p=0.149) between EG and CG. In summary, with minor exceptions, we demonstrated the effectiveness of a multipurpose exercise protocol dedicated to early-postmenopausal women on various risk factors and complaints related to the menopausal transition.
Related collections
Most cited references79
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Metabolic syndrome--a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found