- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Laxative and antioxidant effects of ramie ( Boehmeria nivea L .) leaf extract in experimental constipated rats

Read this article at
Abstract
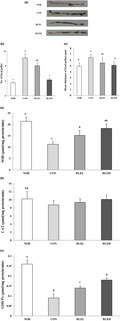
Ramie leaf ( Boehmeria nivea L.) is rich in cellulose, polyphenol compounds, vitamin C, and minerals. The leaves of this plant, which are used for medicinal purposes, have long been reported to have anti‐inflammatory, antioxidant, anticolitis, and antidiabetic effects. We investigated the protective effects of ramie leaf ethanol extract (RLE) against loperamide‐induced constipation and oxidative stress in rats. Male Sprague‐Dawley rats were administered 200 or 400 mg/kg body weight of RLE (RLEL and RLEH groups) by gavage, while normal (NOR) and control (CON) rats received saline. Loperamide (4.0 mg/kg, twice per day) was injected subcutaneously to induce constipation in RLEL, RLEH, and CON groups. Total fecal number, wet weight, and water content decreased, while the total number of loperamide‐induced fecal pellets in the distal colon increased with administration of RLE in a dose‐dependent manner. Gastrointestinal transit time was more greatly reduced in RLE‐treated groups than in the CON group. Serum total cholesterol (TC) level, as well as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, was significantly lower in both RLEL and RLEH groups compared with the CON group. Intestinal mucosa malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2) production decreased significantly in a dose‐dependent manner in the RLE‐treated groups. Loperamide decreased the antioxidant enzyme activity, including that of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH‐Px), while RLE administration increased the antioxidant activity. These results suggest that RLE exerts potent laxative and antioxidant effects in model rats with loperamide‐induced constipation.
Abstract
Oral treat of RLE increased the total number, weight, and water content of rat fecal pellets without causing diarrhea, the incidence of which was decreased by loperamide. Treatment with RLE significantly protected against oxidative stress induced by loperamide intoxication. Phenolic compounds and dietary fiber in RLE may play key roles in the observed anticonstipation and antioxidative effects.
Related collections
Most cited references68
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found