- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of sodium bicarbonate supplementation on the renin-angiotensin system in patients with chronic kidney disease and acidosis: a randomized clinical trial

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Acidosis-induced kidney injury is mediated by the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system, for which urinary renin is a potential marker. Therefore, we hypothesized that sodium bicarbonate supplementation reduces urinary renin excretion in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and metabolic acidosis.
Methods
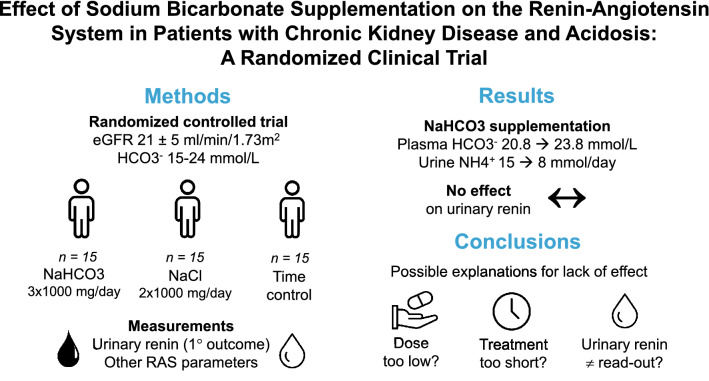
Patients with CKD stage G4 and plasma bicarbonate 15–24 mmol/l were randomized to receive sodium bicarbonate (3 × 1000 mg/day, ~ 0.5 mEq/kg), sodium chloride (2 × 1,00 mg/day), or no treatment for 4 weeks (n = 15/arm). The effects on urinary renin excretion (primary outcome), other plasma and urine parameters of the renin-angiotensin system, endothelin-1, and proteinuria were analyzed.
Results
Forty-five patients were included (62 ± 15 years, eGFR 21 ± 5 ml/min/1.73m 2, plasma bicarbonate 21.7 ± 3.3 mmol/l). Sodium bicarbonate supplementation increased plasma bicarbonate (20.8 to 23.8 mmol/l) and reduced urinary ammonium excretion (15 to 8 mmol/day, both P < 0.05). Furthermore, a trend towards lower plasma aldosterone (291 to 204 ng/L, P = 0.07) and potassium (5.1 to 4.8 mmol/l, P = 0.06) was observed in patients receiving sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate did not significantly change the urinary excretion of renin, angiotensinogen, aldosterone, endothelin-1, albumin, or α1-microglobulin. Sodium chloride supplementation reduced plasma renin (166 to 122 ng/L), and increased the urinary excretions of angiotensinogen, albumin, and α1-microglobulin (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Despite correction of acidosis and reduction in urinary ammonium excretion, sodium bicarbonate supplementation did not improve urinary markers of the renin-angiotensin system, endothelin-1, or proteinuria. Possible explanations include bicarbonate dose, short treatment time, or the inability of urinary renin to reflect intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activity.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Timing of onset of CKD-related metabolic complications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A comparison of treating metabolic acidosis in CKD stage 4 hypertensive kidney disease with fruits and vegetables or sodium bicarbonate.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.