- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficient Adsorption of Tetracycline from Aqueous Solutions by Modified Alginate Beads after the Removal of Cu(II) Ions
Read this article at
Abstract

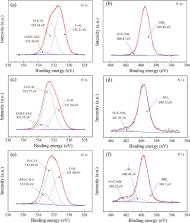
This work dealt with a potential and effective method to reuse modified alginate beads after the removal of Cu(II) ions for efficient adsorption of tetracycline (TC) from aqueous solutions. The modified alginate beads were fabricated by a polyacrylamide (PAM) network interpenetrated in alginate–Ca 2+ network (PAM/CA) decorated with polyethylene glycol as a pore-forming agent. The porous PAM/CA was characterized using scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. The adsorption kinetics, isotherms, adsorption stability, and reusability studies of the adsorbent toward Cu(II) ions were scrutinized. The column performance of porous PAM/CA was tested with Cu(II)-containing electroplating wastewater. After Cu(II) adsorption, the Cu(II)-adsorbed PAM/CA (PAM/CA@Cu) was applied to remove TC from aqueous solutions without any regeneration process. The effects of pH, initial TC concentration, ionic strength, and coexisting ions on the adsorption were also discussed in detail. Compared with many reported adsorbents, the PAM/CA@Cu exhibited an excellent adsorption performance toward TC with a maximum adsorption capacity of 356.57 mg/g predicted by the Langmuir model at pH 5.0 and 30 °C with the absence of coexisting ions. The possible adsorption mechanism of TC onto the PAM/CA@Cu was revealed.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Design and applications of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. A review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Starch, cellulose, pectin, gum, alginate, chitin and chitosan derived (nano)materials for sustainable water treatment: A review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found