- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Job preferences of undergraduate nursing students in eastern China: a discrete choice experiment
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Shortage and mal-distribution of nursing human resources is an intractable problem in China. There is an urgent need to explore the job preferences of undergraduate nursing students. The main aim of this study is to investigate the stated preferences of nursing students when choosing a job.
Methods
A discrete choice experiment (DCE) was conducted to assess job preferences of the final year undergraduate nursing students from four medical universities/colleges in Shandong Province, China. Job attributes include location, monthly income, bianzhi (which refers to the established posts and can be loosely regarded as state administrative staffing), career development and training opportunity, work environment and working strength. Mixed logit models were used to analyze the DCE data.
Results
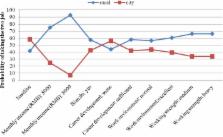
A total of 445 undergraduate nursing students were included in the main DCE analysis. They demonstrated higher preference for a job with higher monthly income, and the probability of choosing a rural job would increase to 92.8% if monthly income increased from RMB 2000 (US$ 296) to RMB 8000 (US$ 1183). They expressed higher stated preferences for a job which required light working strength and with excellent work environment over other non-economic attributes. Among all attributes, location was the least important attribute. Subgroup analysis showed that students who came from city or county and whose family income was more than RMB 50 000 (US$ 7396) were significantly willing to pay more monthly income for a job in city.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Sample Size Requirements for Discrete-Choice Experiments in Healthcare: a Practical Guide

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Staffing remote rural areas in middle- and low-income countries: A literature review of attraction and retention
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found