- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Institutional analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic lymph node metastases
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
In limited metastatic burden of disease, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) has been shown to achieve high local control rates. It has been hypothesized that SBRT may translate to a better quality of life by delaying the need for systemic chemotherapy and possibly increasing survival. There is limited published literature on the efficacy of SBRT in limited nodal metastases. The primary aim is to review institutional outcomes of patients with solitary or oligometastatic lymph nodes treated with SBRT.
Methods
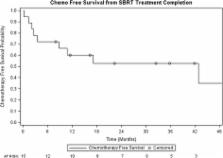
A retrospective study of patients treated with SBRT to metastatic lymph nodes (March 2010–June 2015) was conducted. Endpoints of this study were local control (LC), chemotherapy-free survival (CFS) following SBRT, toxicities, progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results
Eighteen patients with a mean age of 65 years underwent SBRT to metastatic lymph nodes. Median follow-up was 33.6 months. There were four hepatocellular carcinoma, seven colorectal, four pancreatic, one esophageal, one gallbladder and one lung primary. Eleven (61%) patients had lymph node metastases at initial presentation of metastatic disease. Seven patients (39%) had systemic therapy prior to SBRT, with five patients receiving two lines of chemotherapy. Eight patients had solitary metastatic disease at the time of radiotherapy. All patients had <5 metastases. Median size of lymph node metastases was 1.95 cm (range: 0.8–6.2 cm). RT doses were 31 to 60 Gy in four to ten fractions, with 44% of patients receiving 35 Gy in 5 fractions. At 1 year, LC was 94% and CFS from SBRT was 60%. One-year PFS and OS were 39% and 89% respectively. There were no grade 3 or higher toxicities.
Conclusions
In this single institution study, SBRT to oligometastatic lymph nodes provided excellent LC and a moderate chemotherapy-free interval with minimal toxicities. Disease progression remains prominent in these patients and larger studies are warranted to identify those who benefit most from SBRT.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oligometastases revisited.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effect of surgical margin status on survival and site of recurrence after hepatic resection for colorectal metastases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found