- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Novel Therapeutic Targets in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose of Review
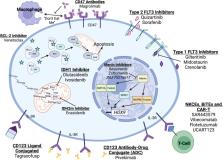
This review seeks to identify and describe novel genetic and protein targets and their associated therapeutics currently being used or studied in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Recent Findings
Over the course of the last 5–6 years, several targeted therapies have been approved by the FDA, for the treatment of both newly diagnosed as well as relapsed/refractory AML. These novel therapeutics, as well as several others currently under investigation, have demonstrated activity in AML and have improved outcomes for many patients.
Summary
Patient outcomes in AML have slowly improved over time, though for many patients, particularly elderly patients or those with relapsed/refractory disease, mortality remains very high. With the identification of several molecular/genetic drivers and protein targets and development of therapeutics which leverage those mechanisms to target leukemic cells, outcomes for patients with AML have improved and continue to improve significantly.
Related collections
Most cited references78
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found