- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pregnancy outcomes among Indian women: increased prevalence of miscarriage and stillbirth during 2015–2021
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Pregnancy outcome is an important health indicator of the quality of maternal health. Adverse pregnancy outcomes is a major public health problem, which can lead to poor maternal and neonatal outcomes. This study investigates the trends in pregnancy outcomes prevalent during 2015–2021 in Indian women.
Methods
The study analysed the data presented in the fourth (2015-16) and fifth (2019-21) rounds of National Family Health Survey (NFHS). The absolute and relative changes in the birth outcomes of last pregnancy during the five years preceding the surveys were estimated using data collected from 195,470 women in NFHS-4 and from 255,549 women in NFHS-5.
Results
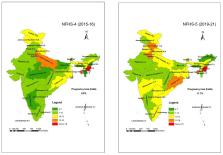
Livebirth decreased by 1.3 points (90.2% vs. 88.9%), and nearly half of the Indian states/UTs (n = 17/36) had lower than the national average of livebirth (88.9%) reported during 2019-21. A higher proportion of pregnancy loss was noted, particularly miscarriages increased in both urban (6.4% vs. 8.5%) and rural areas (5.3% vs. 6.9%), and stillbirth increased by 28.6% (0.7% vs. 0.9%). The number of abortions decreased (3.4% vs. 2.9%) among Indian women. Nearly half of the abortions were due to unplanned pregnancies (47.6%) and more than one-fourth (26.9%) of abortions were performed by self. Abortions among adolescent women in Telangana was eleven times higher during 2019-21 as compared to 2015-16 (8.0% vs. 0.7%).
Conclusion
Our study presents evidence of a decrease in the livebirth and an increase in the frequency of miscarriage and stillbirth among Indian women during 2015–2021. This study emphasises that there is a need of regional-specific, comprehensive and quality maternal healthcare programs for improving livebirth among Indian women.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Stillbirths: ending preventable deaths by 2030.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The incidence of abortion and unintended pregnancy in India, 2015

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found