- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
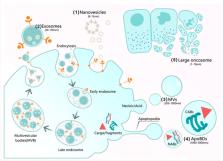
Characteristics of culture-condition stimulated exosomes or their loaded hydrogels in comparison with other extracellular vesicles or MSC lysates
Read this article at
Abstract
Recently, it has become popular to study the use of extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by stem cells to repair damaged tissues or lost cells. Various cell types and physiological fluids release EVs, and they play an important role in cell-to-cell communication. Moreover, EVs have been implicated in important processes, such as immune responses, homeostasis maintenance, coagulation, inflammation, cancer progression, angiogenesis, and antigen presentation. Thus, EVs participate in both physiological and pathological progression. The main classes of EVs include exosomes, microvesicles (MVs), and apoptotic bodies (ApoBDs). Exosomes, which carry a mass of signal molecules such as RNA, DNA, proteins, and lipids, are the most important of these EVs subsets. Currently, exosomes are generating substantial interest in the scientific community. Exosomes loaded hydrogels or under different cultural environments exhibit different properties and functions. Therefore, the exosomes obtained from different sources and conditions are worth reviewing. More importantly, no review article has compared the different EVs, such as exosomes, MVs, ApoBDs, and mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) lysates, which are special soluble substances. The differentiation between EVs and MSC lysates is a logical approach. Accordingly, this review provides an update on the latest progress in studying the roles of culture-condition stimulated exosomes or their loaded hydrogels and the differentiation between exosomes, MVs, ApoBDs, and MSC lysates. Published studies were retrieved from the PubMed® database for review.
Related collections
Most cited references136
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Exosomes Facilitate Therapeutic Targeting of Oncogenic Kras in Pancreatic Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found