- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Developmental Competence of Vitrified-Warmed Bovine Oocytes at the Germinal-Vesicle Stage is Improved by Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Modulators during In Vitro Maturation
Read this article at
Abstract
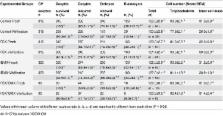
Cryopreservation of mature oocytes and embryos has provided numerous benefits in reproductive medicine. Although successful cryopreservation of germinal-vesicle stage (GV) oocytes holds promise for further advances in reproductive biology and clinical embryology fields, reports regarding cryopreservation of immature oocytes are limited. Oocyte survival and maturation rates have improved since vitrification is being performed at the GV stage, but the subsequent developmental competence of GV oocytes is still low. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of supplementation of the maturation medium with cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) modulators on the developmental competence of vitrified-warmed GV bovine oocytes. GV oocytes were vitrified-warmed and cultured to allow for oocyte maturation, and then parthenogenetically activated or fertilized in vitro. Our results indicate that addition of a cAMP modulator forskolin (FSK) or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) to the maturation medium significantly improved the developmental competence of vitrified-warmed GV oocytes. We also demonstrated that vitrification of GV oocytes led to a decline in cAMP levels and maturation-promoting factor (MPF) activity in the oocytes during the initial and final phases of maturation, respectively. Nevertheless, the addition of FSK or IBMX to the maturation medium significantly elevated cAMP levels and MPF activity during IVM. Taken together, our results suggest that the cryopreservation-associated meiotic and developmental abnormalities observed in GV oocytes may be ameliorated by an artificial increase in cAMP levels during maturation culture after warming.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Novel signaling mechanisms in the ovary during oocyte maturation and ovulation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Over 900 oocyte cryopreservation babies born with no apparent increase in congenital anomalies.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found