- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Myrica esculenta Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don: A Natural Source for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Read this article at
Abstract
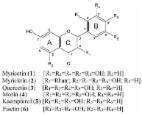
Myrica esculenta (Myricaceae) is a popular medicinal plant most commonly found in the sub-tropical Himalayas. It is widely used in folk medicine to treat several ailments such as asthma, cough, chronic bronchitis, ulcers, inflammation, anemia, fever, diarrhea, and ear, nose, and throat disorders. Due to its multidimensional pharmacological and therapeutic effects, it is well recognized in the ayurvedic pharmacopeia. However, the recent upsurge in M. esculenta use and demand has led to illicit harvesting by the horticultural trade and habitat loss, pushing the plant to the brink of extinction. Thus, the present review aims to provide updated information on M. esculenta botany, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological effects, toxicity, and conservation methods, as well as also highlight prospective for future research. Particular emphasis is also given to its antioxidant potential in health promotion. In-depth literature was probed by searching several sources via online databases, texts, websites, and thesis. About 57 compounds were isolated and identified from M. esculenta, and the available reports on physicochemical parameters, nutritional and high-performance thin-layer chromatography analysis of bioactive plant parts are portrayed in a comparative manner. Friendly holistic conservation approaches offered by plant biotechnology applications, such as micropropagation, germplasm preservation, synthetic seed production, and hairy root technologies are also discussed. Nonetheless, further studies are needed to propose the mechanistic role of crude extracts and other bioactives, and even to explore the structure–function relationship of active components.
Related collections
Most cited references105
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Myricetin: A Dietary Molecule with Diverse Biological Activities
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The in vitro antibacterial activity of dietary spice and medicinal herb extracts.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of flavonoids
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.