- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Associations of non-traditional cardiovascular risk factors and body mass index with metabolic syndrome in the Chinese elderly population
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS), a clustering of traditional cardiovascular risk factors (CVRF), is currently one of the major global public health burdens. However, associations between MetS and non-traditional CVRF represented by uric acid (UA), homocysteine (HCY) and hypersensitive C-reactive protein (HsCRP) have not been well explored in the elderly population, especially when considering body mass index (BMI).
Methods
Participants from the Shanghai Elderly Cardiovascular Health (SHECH) study cohort in 2017 were analyzed. MetS was defined using the modified American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Logistic regression models were used to assess associations of non-traditional CVRF, BMI with MetS.
Results
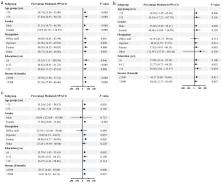
Of the 4360 participants analyzed, 2378 (54.5%) had MetS, the mean (SD) UA was 331 (86) µmol/L, and the median (IQR) HCY and HsCRP were 15 (13–18) µmol/L and 1.0 (0.5–2.1) mg/L, respectively. Participants with higher non-traditional CVRF tended to have a higher significant risk of MetS ( P < 0.001), which did not changed substantially in most population subgroups ( P-interaction > 0.05). BMI mediated 43.89% (95%CI: 30.38–57.40%), 37.34% (95% CI: 13.86–60.83%) and 30.99% (95%CI: 13.16–48.83%) of associations of hyperuricemia (HUA), hyperhomocysteinemia (HHCY) and high HsCRP (HHsCRP) with MetS, respectively. Abnormal non-traditional CVRF combined with overweight/obesity greatly increased MetS risk (adjusted OR(95%CI): HUA + Overweight: 5.860(4.059-8.461); 6.148(3.707–10.194); HHCY + Overweight: 3.989(3.107-5.121); HHCY + Obese: 5.746(4.064–8.123); HHsCRP + Overweight: 4.026(2.906-5.580); HHsCRP + Obese: 7.717(4.508–13.210)).
Conclusions
In the Chinese elderly population, HUA, HHCY, and HHsCRP were all significantly and independently associated with MetS, supporting the potential of focusing on non-traditional CVRF interventions for preventing and controlling MetS. BMI played moderate mediating roles in associations between non-traditional CVRF and MetS, and abnormal non-traditional CVRF combined with overweight/obesity had significant synergistic effects on MetS risk, highlighting the importance of better weight management in the elderly population.
Related collections
Most cited references75
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found