- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Case of Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Pneumopericardium in a Young Adult
Read this article at
Abstract
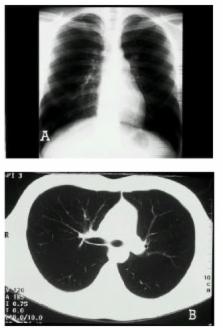
Spontaneous medialstinal emphysema (pneumomediastinum) and pneumopericardium may be defined as the presence of free air or gas in the mediastinal structures and in the pericardial sac without an apparent precipitating cause. It most frequently occurs in young healthy adults without serious underlying pulmonary disease.
Although pneumomediastinum and pneumopericardium is often asymptomatic, it may cause pain in the neck and chest, dysphonia and shortness of breath. Treatment is supportive unless the patient has a history of trauma from foreign body aspiration. The course of spontaneous pneumomediastinum and pneumopericardium is usually benign and self-limited.
A case of spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium and subcutaneous emphysema in a 20-year-old male is reported in this paper.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pneumomediastinum: old signs and new signs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found