- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identification of novel transcripts and noncoding RNAs in bovine skin by deep next generation sequencing
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Deep RNA sequencing (RNAseq) has opened a new horizon for understanding global gene expression. The functional annotation of non-model mammalian genomes including bovines is still poor compared to that of human and mouse. This particularly applies to tissues without direct significance for milk and meat production, like skin, in spite of its multifunctional relevance for the individual. Thus, applying an RNAseq approach, we performed a whole transcriptome analysis of pigmented and nonpigmented bovine skin to describe the comprehensive transcript catalogue of this tissue.
Results
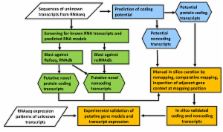
A total of 39,577 unique primary skin transcripts were mapped to the bovine reference genome assembly. The majority of the transcripts were mapped to known transcriptional units (65%). In addition to the reannotation of known genes, a substantial number (10,884) of unknown transcripts (UTs) were discovered, which had not previously been annotated. The classification of UTs was based on the prediction of their coding potential and comparative sequence analysis, subsequently followed by meticulous manual curation. The classification analysis and experimental validation of selected UTs confirmed that RNAseq data can be used to amend the annotation of known genes by providing evidence for additional exons, untranslated regions or splice variants, by approving genes predicted in silico and by identifying novel bovine loci. A large group of UTs (4,848) was predicted to potentially represent long noncoding RNA (lncRNA). Predominantly, potential lncRNAs mapped in intergenic chromosome regions (4,365) and therefore, were classified as potential intergenic lncRNA. Our analysis revealed that only about 6% of all UTs displayed interspecies conservation and discovered a variety of unknown transcripts without interspecies homology but specific expression in bovine skin.
Conclusions
The results of our study demonstrate a complex transcript pattern for bovine skin and suggest a possible functional relevance of novel transcripts, including lncRNA, in the modulation of pigmentation processes. The results also indicate that the comprehensive identification and annotation of unknown transcripts from whole transcriptome analysis using RNAseq data remains a tremendous future challenge.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found