- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Cross-platform Toolkit for Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics
Read this article at
Abstract
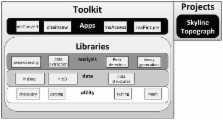
Mass-spectrometry-based proteomics has become an important component of biological research. Numerous proteomics methods have been developed to identify and quantify the proteins in biological and clinical samples 1 , identify pathways affected by endogenous and exogenous perturbations 2 , and characterize protein complexes 3 . Despite successes, the interpretation of vast proteomics datasets remains a challenge. There have been several calls for improvements and standardization of proteomics data analysis frameworks, as well as for an application-programming interface for proteomics data access 4, 5 . In response, we have developed the ProteoWizard Toolkit, a robust set of open-source, software libraries and applications designed to facilitate proteomics research. The libraries implement the first-ever, non-commercial, unified data access interface for proteomics, bridging field-standard open formats and all common vendor formats. In addition, diverse software classes enable rapid development of vendor-agnostic proteomics software. Additionally, ProteoWizard projects and applications, building upon the core libraries, are becoming standard tools for enabling significant proteomics inquiries.
Related collections
Most cited references9

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
mzML—a Community Standard for Mass Spectrometry Data*
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
XCMS2: processing tandem mass spectrometry data for metabolite identification and structural characterization.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
