- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical inertia on insulin treatment intensification in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients of a tertiary public diabetes center with limited pharmacologic armamentarium from an upper-middle income country
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Clinical inertia is related to the difficulty of achieving and maintaining optimal glycemic control. It has been extensively studied the delay of the period to insulin introduction in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. This study aims to evaluate clinical inertia of insulin treatment intensification in a group of T2DM patients followed at a tertiary public Diabetes Center with limited pharmacologic armamentarium (Metformin, Sulphonylurea and Human Insulin).
Methods
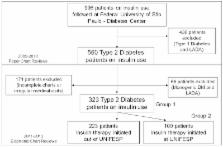
This is a real life retrospective record based study with T2DM patients. Demographic, clinical and laboratory characteristics were reviewed. Clinical inertia was considered when the patients did not achieve the individualized glycemic goals and there were no changes on insulin daily dose in the period.
Results
We studied 323 T2DM patients on insulin therapy (plus Metformin and or Sulphonylurea) for a period of 2 years. The insulin daily dose did not change in the period and the glycated hemoglobin (A1c) ranged from 8.8 + 1.8% to 8.7 ± 1.7% (basal vs 1st year; ns) and to 8.5 ± 1.8% (basal vs 2nd year; p = 0.035). The clinical inertia prevalence was 65.8% (basal), 61.9% (after 1 year) and 58.2% (after 2 years; basal vs 1st year vs 2nd year; ns). In a subgroup of 100 patients, we also studied the first 2 years after insulin introduction. The insulin daily dose ranged from 0.22 ± 0.12 to 0.32 ± 0.24 IU/kg of body weight/day (basal vs 1st year; p < 0.001) and to 0.39 ± 0.26 IU/kg of body weight/day (basal vs 2nd year; p < 0.05). The A1c ranged from 9.6 + 2.1% to 8.6 + 2% (basal vs 1st year; p < 0.001) and to 8.7 + 1.7% (1st year vs 2nd year; ns). The clinical inertia prevalence was 78.5% (at the moment of insulin therapy introduction), 56.2% (after 1 year; p = 0.001) and 62.2% (after 2 years; ns).
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Glycemic Control With Diet, Sulfonylurea, Metformin, or Insulin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusProgressive Requirement for Multiple Therapies (UKPDS 49)

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Structured Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Significantly Reduces A1C Levels in Poorly Controlled, Noninsulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found