- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Preparation, structure and up-conversion luminescence properties of novel cryolite K 3YF 6:Er 3+, Yb 3+
Read this article at
Abstract
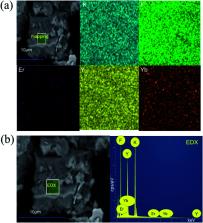
Cryolite is a suitable host for up-conversion luminescent materials due to its low phonon energy and good optical transparency. In this work, a novel up-conversion material K 3YF 6:Yb 3+, Er 3+ with a cryolite structure was prepared successfully by a solid state method. The crystal structure, morphology, composition and up-conversion luminescence properties of the as-prepared sample were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and fluorescence spectrometer in detail. K 3YF 6:Er 3+, Yb 3+ has a cryolite structure. Under 980 nm excitation, the as-prepared sample can generate slight green emission at 524 and 546 nm (attributed to 2H 11/2 → 4I 15/2 transition, 4S 3/2→ 4I 15/2 transition of Er 3+) and strong red emission at 661 and 672 nm (corresponding to 4F 9/2 → 4I 15/2 transition, 4I 9/2 → 4I 15/2 transition of Er 3+). All the green and red up-conversion emission of K 3YF 6:Er 3+, Yb 3+ transfer and electronic transition process of the red and green light the sample emitted, the possible luminescence mechanism is discussed in this paper.
Abstract
Single-phase up-conversion luminescent materials K 3YF 6:Er 3+, Yb 3+ with cryolite structure were obtained for the first time.

Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Broadband dye-sensitized upconversion of near-infrared light
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Enhancing multiphoton upconversion through energy clustering at sublattice level
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found