- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A broadband near-infrared phosphor BaZrGe 3O 9:Cr 3+: luminescence and application for light-emitting diodes
Read this article at
Abstract
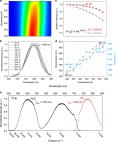
A broadband NIR luminescence material BaZrGe 3O 9:Cr 3+ was designed, the crystal field parameters and Huang–Rhys factor were calculated to evaluate the luminescence. The potential application for NIR pc-LED was demonstrated.
Abstract
Recently, near-infrared (NIR) phosphor-converted light-emitting diodes (pc-LEDs) have attracted considerable interest in the research field worldwide. As the key material, broadband NIR phosphors have become a research hotspot. Herein, a series of Cr 3+-doped BaZrGe 3O 9 phosphors were successfully designed via nonequivalent substitution. The phosphors exhibited a broadband emission extending from 700 nm to 1200 nm (FWHM = 159 nm) with a maximum of ∼830 nm in the first biological window. To optimize the luminescence properties, the relationships between the doping concentration and crystal structure, luminescence spectra, decay curves were discussed. More importantly, the crystal field parameters D q, B and Huang–Rhys factor were calculated, and the results may provide insight into factors determining and modifying the luminescence properties of the materials. The persistent luminescence of Cr 3+ could also be realized, and the luminescence mechanism was proposed. Moreover, a pc-LED prototype was fabricated by combining the BaZrGe 3O 9:Cr 3+ phosphor with a blue LED chip, and the potential application for broadband NIR pc-LEDs was discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Strategies to approach high performance in Cr 3+ -doped phosphors for high-power NIR-LED light sources
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Super Broadband Near-Infrared Phosphors with High Radiant Flux as Future Light Sources for Spectroscopy Applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found