- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Assessment of Third Molar Impaction Pattern and Associated Clinical Symptoms in a Central Anatolian Turkish Population
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the pattern of third molar impaction and associated symptoms in a Central Anatolian Turkish population.
Material and Methods
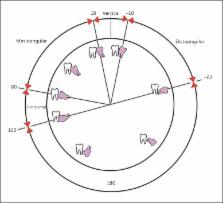
A total of 2,133 impacted third molar teeth of 705 panoramic radiographs were reviewed. The positions of impacted third molar teeth on the panoramic radiographs were documented according to the classifications of Pell and Gregory and of Winter. The presence of related symptoms including pain, pericoronitis, lymphadenopathy and trismus was noted for every patient. Distributions of obtained values were compared using the Pearson χ 2 test. Nonparametric values were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results
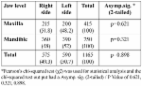
The mean age of the subjects was 30.58 ± 11.98 years (range: 19-73); in a review of the 2,133 impacted third molar teeth, the most common angulation of impaction in both maxillaries was vertical (1,177; 55%). Level B impaction was the most common in the maxilla (425/1,037; 39%), while level C impaction was the most common in the mandible (635/1,096; 61%). Pain (272/705; 39%) and pericoronitis (188/705; 27%) were found to be the most common complications of impaction. Among 705 patients (335 males, 370 females), pericoronitis was more prevalent in males (101; 30%) and usually related to lower third molars (236; 22%). The retromolar space was significantly smaller in females (p < 0.05). Moreover, there was a significant difference in retromolar space for the area of jaw (maxillary: 11.3 mm; mandibular: 14.2 mm) and impaction level (A: 14.7 mm; B: 11.1 mm; C: 10.3 mm; p < 0.05).
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Extraction of impacted mandibular third molars: postoperative complications and their risk factors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Incidence of impacted mandibular and maxillary third molars: a radiographic study in a Southeast Iran population
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found