- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of Combination Maintenance with Pemetrexed and Bevacizumab for Advanced Stage Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of combination maintenance therapy of pemetrexed plus bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Methods
We identified relevant studies by electronic search (Embase, PubMed, Cochrane, and Web of Science from 1 January 1960 to 29 October 2016) and manual search. The primary outcome of interest was progression-free survival (PFS) and secondary end point included overall survival (OS) and toxicities. The data was pooled for quantitative analysis and the final effect size was reported as hazard ratio (HR) for survival outcomes and relative risk (RR) for safety outcomes, both with a random-effects model.
Results
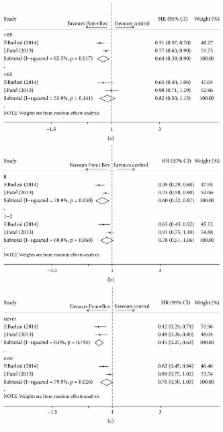
Three randomized controlled trials enrolling 1302 patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer were included in this meta-analysis. An evident PFS improvement (HR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.63–0.83, P < 0.01) was observed in patients with pemetrexed and bevacizumab combination maintenance therapy compared with single-agent maintenance therapy, yet it did not subsequently lead to a significant improvement in OS (HR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.84–1.10, P = 0.66). Our analysis also showed statistically increased risks for provoking grade 3-4 adverse events in patients managed using pemetrexed plus bevacizumab combination (RR = 1.59, 95% CI = 1.07–2.36, P = 0.022).
Conclusions
Pemetrexed plus bevacizumab combination maintenance therapy leads to significant improvement in PFS but not in OS for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, which also increases the risks of grade 3-4 adverse events. Yet, in view of the limitation of existing studies and this meta-analysis, current evidence is not adequate to support routine use of pemetrexed-bevacizumab maintenance.
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found